Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition characterized by the loss of pigment in patches of skin, leading to lighter areas that can be more sensitive to sun exposure. Affecting individuals of all skin types, the exact cause of vitiligo remains unclear, but it is believed to result from an autoimmune response where the body’s immune system attacks melanocytes – the cells responsible for producing melanin. The condition can significantly impact quality of life, leading to psychological and social effects. While topicals, systemic treatments, and surgical options exist for managing vitiligo, phototherapy, particularly using UVB (ultraviolet B) light, has emerged as a beneficial treatment modality.
Understanding UVB Light
Ultraviolet light is divided into three categories based on wavelength: UVA, UVB, and UVC. UVB rays, with wavelengths ranging from 280 to 320 nanometers, are primarily responsible for causing sunburn and play a crucial role in the synthesis of vitamin D in the skin. Unlike UVA rays, which penetrate deeper into the skin and are associated with skin aging and wrinkling, UVB rays affect the outer layers of the skin and are more significant in the treatment of conditions like vitiligo.
Mechanism of Action
The therapeutic use of UVB light in vitiligo treatment is based on its ability to stimulate melanocyte activity. When exposed to UVB light, skin cells undergo a process known as photobiomodulation, which can enhance the proliferation and function of melanocytes. This process promotes repigmentation of the depigmented patches by encouraging the migration and maturation of these cells while also reducing the number of activated T-cells that contribute to the autoimmune process. Thus, controlled exposure to UVB light can help in restoring skin colour and improving overall skin appearance in individuals with vitiligo.
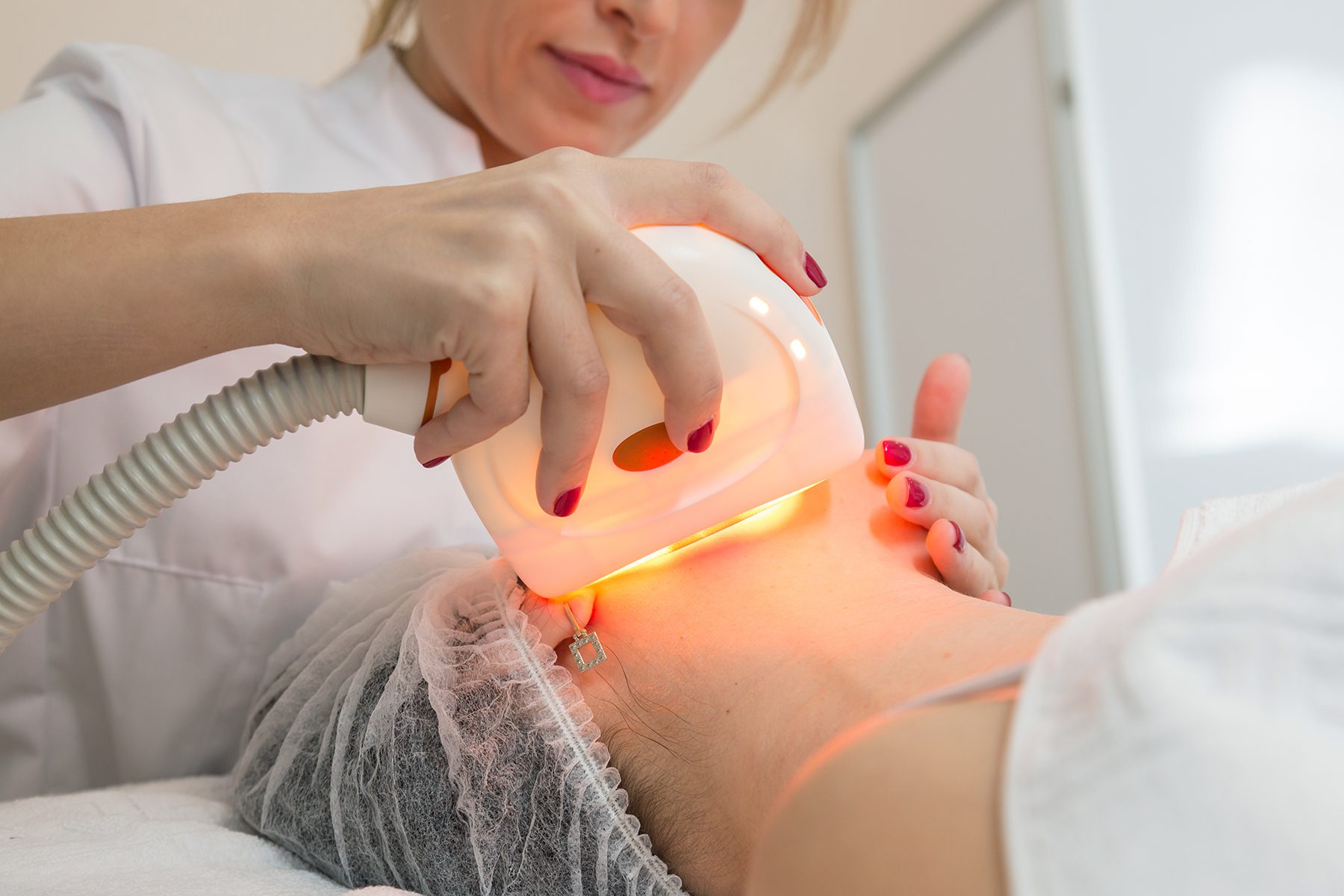
Types of UVB Therapy
UVB therapy for vitiligo can be delivered through two primary methods:
- Broadband UVB Phototherapy:
This involves the use of a conventional light box that emits a broad spectrum of UVB light. Treatments typically take place two to three times a week and require careful monitoring to minimize the risk of skin damage.
- Narrowband UVB Phototherapy:
This method employs a narrow band of UVB wavelengths (specifically around 311-313 nm) that has shown more effective results for repigmentation while causing less skin damage compared to broadband UVB. Narrowband therapy is increasingly becoming the standard for vitiligo treatment, with sessions often lasting around 5 to 10 minutes.
Treatment Protocols
When initiating UVB therapy for vitiligo, practitioners typically assess the extent and distribution of depigmented areas. A customized treatment plan may include:
- Frequency of Sessions: Commonly, patients receive 2-3 sessions per week.
- Duration: Initial exposure times are usually brief, gradually increasing as the skin adapts to light exposure. This helps to minimize the risk of side effects such as erythema (redness).
- Combination Therapies: In some cases, UVB therapy may be used alongside other treatment modalities, such as topical corticosteroids or calcipotriene (a vitamin D analogue), to enhance results.
Efficacy of UVB Treatment
Numerous studies indicate that UVB phototherapy can significantly improve the appearance of vitiligo. It has been reported that about 50-70% of patients experience noticeable repigmentation, especially when treatment begins early after the onset of the condition. The areas most likely to respond positively include the face, neck, and upper trunk, while extremities and areas that have been depigmented for longer periods typically respond less favourably.
Side Effects and Considerations
While UVB therapy is generally considered safe, there are potential side effects to be mindful of, including:
- Skin Redness and Irritation: Like sunburn, this can occur post-treatment.
- Photosensitivity: Patients may become more sensitive to sunlight and could require diligent sun protection measures.
- Long-Term Risks: There is a theoretical risk of skin cancer with extensive UV exposure; however, the benefits often outweigh the risks when treatment is conducted under medical supervision.
Practical Tips for Patients
For those undergoing UVB therapy for vitiligo, adherence to treatment protocols is key. Here are practical tips:
- Sunscreen Use: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen of SPF 30 or higher to protected skin areas to prevent photo-damage.
- Skin Care Routine: Maintain a gentle skin care regimen to avoid further irritation. Use mild soaps and moisturizers.
- Diet and Nutrition: Incorporate foods rich in antioxidants to help support skin health.
- Regular Follow-ups: Attend follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Recent Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research continues to explore the full potential of UVB therapy for vitiligo, including combination treatments with emerging therapies such as JAK inhibitors. We can expect more tailored and effective treatment strategies to arise as our understanding of the pathophysiology and treatment of vitiligo evolves. In addition, advancements in home-based UVB devices provide an avenue for increased accessibility to phototherapy, enabling patients to safely manage their condition in the comfort of their own homes.
Conclusion
UVB phototherapy represents a promising and effective option for the treatment of vitiligo, providing hope for individuals seeking to regain their skin’s natural pigmentation. By understanding the mechanisms, protocols, and potential side effects associated with UVB treatment, patients can make informed decisions about their health and work alongside their healthcare providers to achieve the best outcomes. Through continued research and technological advancements, the future looks bright for those affected by vitiligo as they seek restoration and empowerment in their skin health journey.